Issues
To effectively design products that are environmentally, socially and financially sustainable, it is essential that all members of the design team have at least a basic understanding of the key issues in all three areas. Key issues are therefore outlined below:
It is important to note that there is considerable overlap between some issues.
Environmental Issues
 |
Acidification Increased acidity of air, water and soil
|
 |
Air Pollution Contamination of the air with harmful gases and particles
|
 |
Global Warming The rising temperature of the Earth’s atmosphere
|
 |
Land Degradation Reduction in the ability of soil to support life
|
 |
Ozone Depletion Destruction of the Ozone Layer located 20-50km above Earth’s surface
|
 |
Reduced Biodiversity Loss of variety in the natural world
|
 |
Solid Waste Scrap material with no useful function
|
 |
Water Pollution Contamination of natural water systems such as rivers. lakes, oceans and groundwater with hazardous substances
|
Social Issues
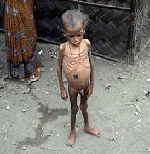 |
Poverty Lacking sufficient wealth to meet basic human needs
|
 |
Exploitation Unfair treatment of people
|
 |
Ill Health – Mental and Physical Poor condition of the mind or body
|
 |
Lack of Essential Services Insufficient systems to provide for the essential needs of the population
|
 |
Civil Unrest Rebellion of citizens against systems and organisations
|
 |
Crime Committing of acts forbidden by law
|
 |
Depression Feeling of unhappiness and hopelessness
|
Financial Issues
 |
Liabilities Legal responsibility for the costs and damages caused by operations
|
 |
Finite Resources Consumption of resources that are in short supply
|
 |
Customer Loyalty Desire of customers to use the products/services of organisation over those of competitors
|
 |
Waste – “muda” Non-productive consumption of material and human resources
|
 |
Inconsistent Revenues Unpredictable and unreliable revenue streams
|
 |
Declining Customer Value Reduction in the value of customer base
|
 |
Rising Costs Increasing cost of human and material resources
|
 |
Competition Struggle to survive against other organisations fighting for the same customers
|

